Reverse Osmosis Water Filter System Animation: In today’s health-conscious society, ensuring access to pure and clean water is a top priority. We recognize this necessity and present to our readers an insightful exploration into the reverse osmosis water filter system animation, a cutting-edge technology in water purification. Reverse osmosis stands out as a highly efficient method for removing impurities, including dissolved salts, bacteria, and viruses, from water through a semi-permeable membrane. This process not only enhances the taste but also the safety of drinking water, making it an integral part of modern water filtration systems.
In this article, we will delve into the mechanics behind reverse osmosis, offering our audience a detailed step-by-step animation of the reverse osmosis process, which illuminates the science and engineering of this advanced purification system. From understanding the core principles of reverse osmosis technology to exploring its practical applications in various sectors, we aim to provide comprehensive coverage. Additionally, our discussion will extend to the importance of components such as membranes, pressure vessels, and the overall filtration process, ensuring readers gain a full understanding of how reverse osmosis water filter systems work to produce clean, safe, and palatable drinking water.
Understanding Reverse Osmosis Technology
Basic Principles
Reverse osmosis (RO) is a sophisticated technology that removes contaminants from water by pushing it under pressure through a semi-permeable membrane . Unlike simple filtration, the process of osmosis naturally occurs when a weaker saline solution migrates to a stronger saline solution, such as plant roots absorbing water from the soil . However, RO reverses this natural flow by applying energy to the more saline solution, effectively filtering out up to 99% of dissolved salts, particles, and microbes from the water .
How It Differs from Other Filtration Methods
RO technology differs significantly from other filtration methods primarily through its use of a semi-permeable membrane that allows only water molecules to pass while blocking larger molecules or ions . This selective permeability ensures that contaminants such as dissolved salts, bacteria, and certain chemicals are effectively removed from the water . Unlike ordinary filters that physically trap contaminants, RO systems apply pressure to overcome osmotic pressure, pushing water through the RO membrane and leaving impurities behind . This results in purified water on one side of the membrane and concentrated contaminants on the other, which are then flushed away.
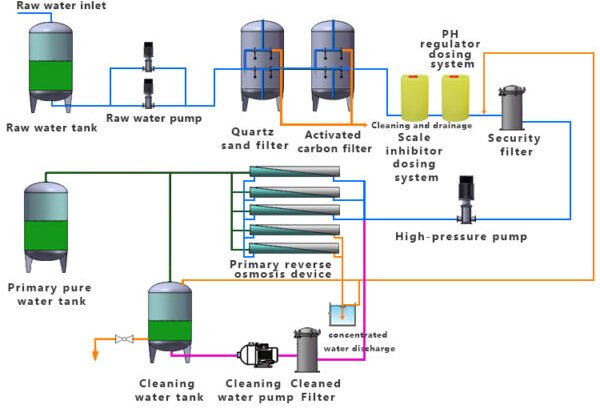
Step-by-Step Animation of the Reverse Osmosis Process
Initial Water Entry
In our reverse osmosis system, the process begins when water is introduced into the pressure vessel. Initially, the water flows over the surface of a tightly wound membrane, moving from one end of the vessel to the other . This initial stage is crucial as it starts the separation process where water is prepared for detailed filtration.
Membrane Filtration
As the water travels through the vessel, it encounters the membrane layer, which is exceptionally thin yet effective. This layer allows water molecules to permeate through while blocking larger compounds based on their size, shape, and charge. Contaminants like salts, organic compounds, microorganisms, viruses, and pharmaceuticals are effectively prevented from passing through . The strategic placement of the membrane sheets, combined with feed channel spacers, ensures turbulence and space for feed water, enhancing the filtration efficiency .
Collection of Purified Water
The pure water, or permeate, that successfully passes through the membrane collects in the core tube and exits from one end of the pressure vessel. Simultaneously, water that does not permeate becomes highly concentrated with salts and other substances, known as concentrate, which exits through a different outlet. This concentrate can be redirected into other pressure vessels for further purification, maximizing the recovery of purified water . This systematic collection and redirection underline the efficiency of reverse osmosis systems in producing high-quality water for various uses.

Practical Applications of Reverse Osmosis Systems
Household Use
We have discovered that incorporating a reverse osmosis (RO) system at home significantly enhances water quality and taste, encouraging our family to drink more water. It’s a sustainable step away from plastic bottles, reducing waste and ongoing costs associated with buying bottled water . Moreover, the system’s energy efficiency means we’re not only saving on utilities but also contributing to a smaller carbon footprint.
Commercial and Industrial Applications
In commercial settings, reverse osmosis systems are indispensable. They ensure consistent water quality crucial for industries like food and beverage, where taste and safety are paramount . For industrial applications, these systems are vital in processes that require pure water devoid of minerals and contaminants, such as in pharmaceuticals and electronics manufacturing . By installing RO systems, industries can prevent equipment damage and downtime due to scaling and other issues caused by hard water.
Environmental Benefits
One of the most compelling advantages of reverse osmosis systems is their minimal environmental impact. These systems do not require harmful chemicals for operation, significantly reducing hazardous wastewater . This aspect is crucial for industries committed to sustainable practices, as it helps in maintaining ecological balance and supports corporate responsibility towards environmental conservation.
By implementing reverse osmosis technology, we are not only ensuring superior water purity but also embracing an eco-friendly approach to water use in both residential and industrial contexts.
Conclusion
Through this comprehensive exploration of reverse osmosis water filter systems, we’ve delved into the intricate mechanics behind this transformative technology, providing a clearer understanding of its pivotal role in purifying water. The step-by-step animation offered an illuminating glimpse into the sophisticated process of reverse osmosis, from initial water entry through to the production of clean, safe drinking water. This detailed examination not only underscores the importance of each component, such as membranes and pressure vessels but also highlights the system’s efficacy in filtering out a vast array of contaminants. Furthermore, by covering the practical applications of reverse osmosis systems across household, commercial, and industrial settings, we’ve showcased their versatility and essential contribution to enhancing water quality, efficiency, and sustainability.
In addition to demystifying the technical workings of reverse osmosis systems, our discussion has encapsulated their environmental benefits and the significant impact they have on promoting eco-friendly water use practices. As we strive for cleaner, more sustainable water solutions, the adoption of reverse osmosis technology emerges as a cornerstone in achieving these goals. For those looking to deepen their knowledge on this subject or to explore the potential of reverse osmosis systems further, engaging with seasoned experts like Chunke Water Treatment, with 20 years of dedicated experience in the field, can provide invaluable insights and guidance. To get more information about reverse osmosis water filter system animation, please send us an email. With continued advancements and dedication to water purification excellence, reverse osmosis stands at the forefront of ensuring access to pure, clean drinking water for all.
FAQs
1. How does a reverse osmosis water filter system operate?
A reverse osmosis system first uses a prefilter to remove sediment and chlorine from water. The water is then forced through a semipermeable membrane, which filters out dissolved solids. After passing through the RO membrane, the water is polished by a postfilter before it is delivered to a dedicated faucet for use.
2. Can you describe the reverse osmosis process?
Reverse osmosis is a purification method that filters out ions, unwanted molecules, and larger particles from drinking water. This is achieved by using a partially permeable membrane that allows only the pure solvent (water) to pass through while retaining the solute (contaminants) on the pressurized side of the membrane.
3. What is the simplest explanation of how reverse osmosis works?
In simple terms, reverse osmosis involves forcing water through a semi-permeable membrane. This process leaves contaminants behind, which are then flushed away, while the purified drinking water is collected in a holding tank.
4. Is drinking water from a reverse osmosis system healthy?
Drinking water from a reverse osmosis system is generally considered safe. There is no significant evidence suggesting that water purified through reverse osmosis poses health risks. As long as you maintain a balanced diet and do not have specific health issues like severe acid reflux or gastrointestinal ulcers, reverse osmosis water should not negatively affect your health or wellbeing.




