Industrial water refers to water that is used in various industrial processes, operations, and manufacturing activities. It is a broad term that encompasses water utilized for a wide range of purposes in industrial settings. Industrial water is different from domestic water, which is the water we typically use in our homes for drinking, cooking, cleaning, and other household activities.
Usage of industrial water
Cooling
In industries where machinery generates heat during operation, water is used for cooling purposes to maintain optimal operating temperatures and prevent overheating.
Steam generation
Many industries require steam for various processes, such as in power generation, heating, and sterilization. Industry water is used to produce steam through boilers.
Cleaning and rinsing
Water is used for cleaning and rinsing products, equipment, and machinery in industries like food processing, pharmaceuticals, and electronics manufacturing.
Dilution
In certain manufacturing processes, raw materials are mixed with water to achieve the desired consistency or concentration.
Transportation
Water is used as a medium to transport materials or goods in industries like mining and dredging.
Power generation
Hydropower plants use water to generate electricity through turbines.
Chemical reactions
Some chemical processes require water as a reactant or as a solvent to dissolve substances.
Fire protection
Industrial facilities often have fire suppression systems that use water to control or extinguish fires.
The quality and treatment requirements of industrial water can vary depending on the specific application and the industry’s needs. In some cases, industrial water may need to undergo purification or treatment to meet certain standards and prevent contamination of products or equipment. So, proper management of industrial water is essential to ensure efficient and sustainable industrial operations while minimizing environmental impact.
Industrial Water and Production Process
Industrial water plays a crucial role in various manufacturing processes, from fabricating and processing to diluting and cooling products. Hence, the proper treatment of industrial water is essential to optimize these processes, reduce operational costs, and ensure the sustainability of water resources. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different aspects of industrial water treatment, including its importance, processes, and the equipment used, accordingly.
The Significance of Industrial Water Treatment
Industrial water treatment is necessary to maintain the quality of water used in manufacturing processes and prevent detrimental effects on equipment and product quality. So, without proper treatment, water can interact with the surfaces of pipes and vessels, leading to scaling, corrosion, and microbial growth. So, these issues can result in increased energy consumption, decreased efficiency, and even system failure.
Scaling and Corrosion Prevention
One of the main objectives of industrial water treatment is to prevent scaling and corrosion. Hence, scaling occurs when dissolved mineral salts in water precipitate and form solid deposits on the surfaces of systems. So, this can reduce heat exchange efficiency, narrow pipe widths, and increase energy consumption. Meanwhile, corrosion, on the other hand, compromises the integrity of plant equipment and can lead to leaks and system failures.
Microbial Control
Untreated cooling water can become a breeding ground for bacteria and other microorganisms. So, these microorganisms can thrive in warm water and organic nutrient-rich environments, such as wet cooling towers. Unmanaged cooling towers have been associated with outbreaks of diseases like Legionnaires’ disease. So, proper water treatment includes measures to control microbial growth and ensure the safety of industrial processes and personnel.
Compliance with Disposal Standards
Industrial processes often generate wastewater that needs to be treated before disposal. So, many industries have onsite facilities to treat their wastewater to comply with local and national regulations. Meanwhile, the treatment processes aim to reduce pollutant concentrations to acceptable levels before the wastewater is discharged into sewage treatment plants, rivers, lakes, or oceans.
Industrial Water Treatment Processes
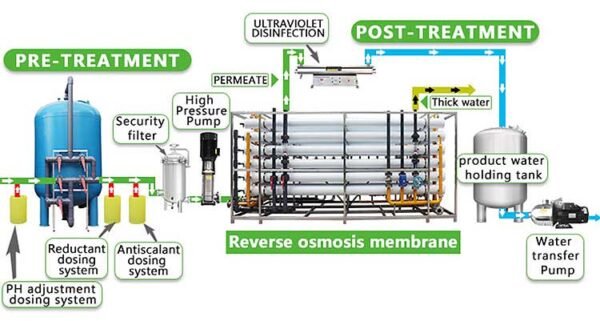
Water treatment involves a combination of processes to achieve the desired water quality for specific applications. So, these processes may include membrane filtration, deaeration, degasification, decarbonation, ion exchange, chemical treatment, and disinfection.
Membrane Filtration
Membrane filtration, commonly known as reverse osmosis, is a process that uses semipermeable membranes to remove molecules, ions, and larger particles from water. Hence, water is forced through the membrane under pressure, leaving behind impurities. So, this process is effective in removing dissolved solids and particulate matter, ensuring high water quality for industrial applications, accordingly.
Deaeration at Industrial Water
Deaeration is the process of removing dissolved gases, primarily oxygen, from water. So, this is important to prevent corrosion in low-pressure boilers. As a result, Steam and water are introduced into a deaerator tower, where steam heats the water to near saturation levels. The dissolved gases are released from the water and vented out, ensuring that the water is free from oxygen and other gases that can cause corrosion, accordingly.
Decarbonation and Degasification
Decarbonation and degasification are essential processes in industrial water treatment. So, these processes remove gases such as carbon dioxide (CO2) and hydrogen sulfide (H2S) from water to prevent scaling and corrosion. Towers are used to expose the water to cross-current airflow, reshaping the water to release the dissolved gases. The efficiency of decarbonation and degasification towers depends on factors such as water temperature, pH adjustment, media type, and airflow volume.
Ion Exchange in Industrial Water
Ion exchange is a process that involves the exchange of ions between a solid resin and the water being treated. This process is commonly used for water softening to remove hardness-causing ions, such as calcium and magnesium. So, it can also be employed for the removal of specific contaminants, such as heavy metals, through selective ion exchange resins.
Chemical Treatment and Disinfection
Chemical treatment is often used in industrial water treatment to address specific water quality issues. So, chemical additives may be employed to control pH, prevent scaling and corrosion, or inhibit microbial growth. Disinfection methods, such as ozonation or ultraviolet (UV) treatment, are used to eliminate harmful microorganisms and ensure the safety of the treated water.
Industrial Water Treatment Equipment
To achieve effective water treatment, specialized equipment is employed at various stages of the treatment process. So, each piece of equipment serves a specific purpose in optimizing water quality and ensuring the efficiency and sustainability of industrial processes.

Pretreatment Equipment
Pretreatment equipment is used to remove larger particles and impurities from the incoming raw water before it undergoes further treatment processes. So, this equipment may include sand filters, carbon filters, and water softeners. So, sand filters help to remove suspended solids, while carbon filters remove organic contaminants and improve taste and odor. Water softeners use ion exchange resins to remove hardness-causing ions and prevent scaling.
Reverse Osmosis Systems
Reverse osmosis (RO) systems are widely used in industrial water treatment for their ability to remove dissolved solids, organic compounds, and other contaminants. These systems utilize semipermeable membranes to separate impurities from water under high pressure. Hence, RO systems are highly effective in producing high-quality water for various applications, including boiler feed systems, steam generation, and incorporation into food and beverage products.
Ultrafiltration (UF)
Ultrafiltration water treatment process that uses a semipermeable membrane to remove suspended solids, colloidal particles, bacteria, and some larger molecules from water. It is a type of membrane filtration technology that operates on the principle of size exclusion, allowing only small molecules and dissolved substances to pass through while blocking larger particles.
In the ultrafiltration process, water is forced through the UF membrane under pressure. So, the membrane has very fine pores, typically in the range of 0.01 to 0.1 microns. Suspended particles and microorganisms that are larger than the pore size of the membrane are rejected and retained on the feed side, while clean, filtered water passes through to the permeate side, accordingly.
Industrial Water Treatment Plants
Industrial water treatment plants are comprehensive facilities designed to handle the treatment of large volumes of water. These plants often incorporate multiple treatment processes, including pretreatment, membrane filtration, disinfection, and chemical dosing. So, they are customized to meet the specific water quality requirements of different industries and ensure the consistent supply of high-quality water for industrial processes.
RO Plants
RO plants, also known as reverse osmosis plants, are specifically designed to remove dissolved solids and contaminants from water through the reverse osmosis process. So, these plants consist of multiple stages, including pretreatment, RO membranes, and post-treatment, accordingly. RO plants are widely used in industries where high-quality water is essential, such as pharmaceuticals, electronics manufacturing, and power generation.
Chunke Water Treatment Systems
Chunke water treatment systems are widely recognized for their reliability and efficiency in industry water treatment. So, these systems utilize advanced technologies and high-quality components to deliver optimal performance in removing impurities and ensuring water quality. Hence, Chunke water treatment systems are designed to be cost-effective, environmentally friendly, and easy to operate, making them a popular choice in industrial settings.
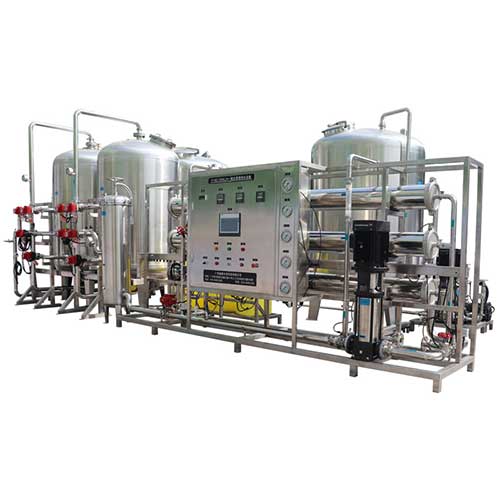

Industrial Reverse Osmosis Plant for Tap Water
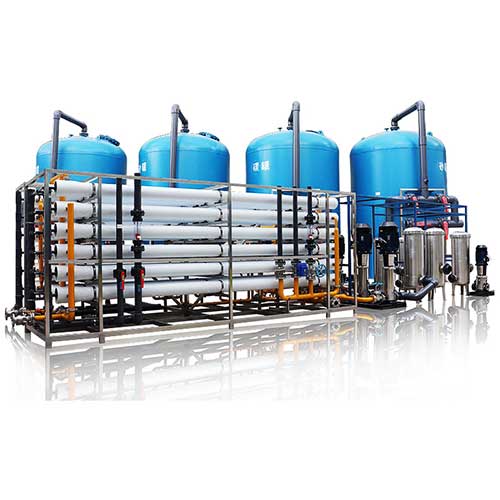

Industrial Reverse Osmosis Plant for Brackish Water
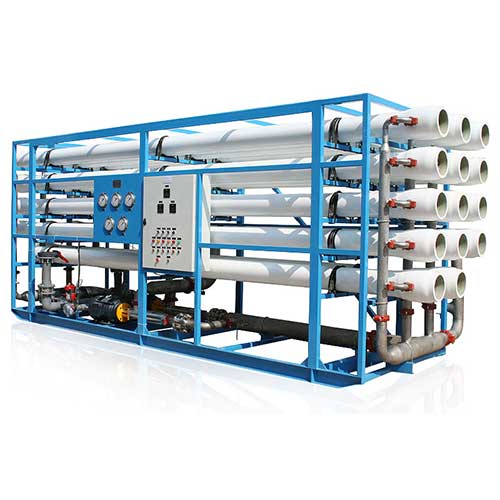

Industrial Reverse Osmosis Plant for Sea Water


