Today, we will introduce to you what’s new in water treatment industry in 2023. Our article has technical details of newest technology in water filtration and purification. Depends on water sources conventional water treatment systems giving solution on Reverse Osmosis, Ultrafiltration, Nanofiltration, Electrodeionization, and combination of flocculation, sedimentation, disinfection.
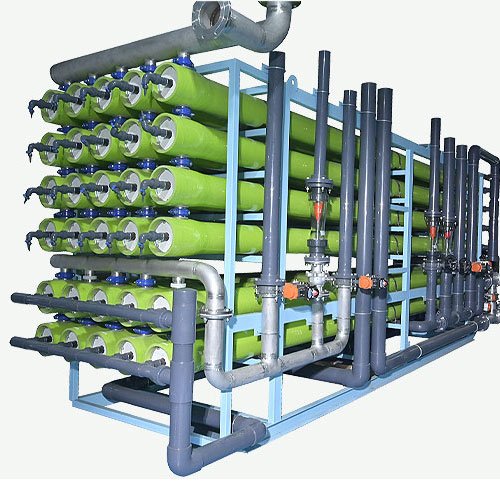

We have plenty of article for reverse osmosis water treatment, ultrafiltration systems, pretreatment systems, water softener system and electrodeionization water treatment system. Now, we look into what’s new in water treatment on scientific side. Some of them cannot be commercial, but do not forget reverse osmosis technology also started in lab. study accordingly.
First we check popular water treatment processes.
Traditional Water Treatment System Technology
In fact, that traditional water treatment systems are based on two types. First, municipal water treatment and second, reverse osmosis technology. Municipal drinking water system has 5 steps for ***filtration systems. They are Flocculation, Coagulation, Sedimentation, Filtration and Disinfection. To more details, please read our artical about ***municipal water treatment. ***Raw water passes these process and then served to community.

Reverse Osmosis RO Water Treatment Technology
Reverse Osmosis RO Water Purifiers are very popular in market. Commercial and Industrial Water RO Purifiers are used by small businesses, large scales factories and governments. Also, now RO water filtration systems becomes very small size, you can install in undersink in your home and get good quality for for dtinking.
In Reverse Osmosis Water Purification System, first, we send raw water to raw water storage tank. Depend on water sources, water treatment companies choose suitable material. Second, from raw water tank to pretreatment filters. Pretreatment water filtration systems can have quartz sand, granular activated carbon (GAC), and ion exchange resin. After, pretreatment, our water comes to cartridge filter housing, then we send water to RO membranes by high pressure pump. So, RO Membrane Technology is responsible to remove unwanted organic and inorganic matters from your source water. Water passes semipermeable reverse osmosis membranes and you get clean and safe treated water. So, to eliminate contamination from outside, we can ad Ultraviolet Radiation UV Sterilizer or Ozone Generator to kill bacteria and viruses accordingly.
Here, there is a video, to show how does reverse osmosis plant work.
How Does RO Water Purification System Work?
This technology is used over 70 years, now we start to explain what’s new in water treatment.
What's New in Water Treatment Technology?
Nanotechnology
Important challenges in the global water situation, mainly resulting from worldwide population growth and climate change, require novel innovative water technologies in order to ensure a supply of drinking water and reduce global water pollution. Against this background, the adaptation of highly advanced nanotechnology to traditional process engineering offers new opportunities in technological developments for advanced water and wastewater technology processes.
When people are searching what’s in water treatment, first, they face to nanotechnology accordingly.
Nanomaterials have unique size-dependent properties related to their high specific surface area (fast dissolution, high reactivity, strong sorption) and discontinuous properties (such as superparamagnetic, localized surface plasmon resonance, and quantum confinement effect). Hence, these specific nano-based characteristics allow the development of novel high-tech materials for more efficient water and wastewater or water treatment processes, namely membranes, adsorption materials, nano catalysts, functionalized surfaces, coatings, and reagents. In future, wastewater treatment plants will use nanomaterials more and more.
Adsorption
Adsorption is the capability of all solid substances to attract to their surfaces molecules of gases or solutions with which they are in close contact. Solids that are used to adsorb gases or dissolved substances are called adsorbents, and the adsorbed molecules are usually referred to collectively as the adsorbate. What’s new in water treatment is important question and here some special nano materials.
- carbon-based nanoadsorbents ie, carbon nanotubes (CNTs)
- metal-based nanoadsorbents
- polymeric nanoadsorbents
- zeolites.
Carbon nanotubes
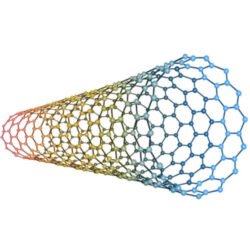
CNTs are allotropes of carbon with a cylindrical nanostructure. Depending on their manufacturing process, CNTs are categorized as single-walled nanotubes and multiwalled nanotubes, respectively. Besides having a high specific surface area, CNTs possess highly assessable adsorption sites and an adjustable surface chemistry. Due to their hydrophobic surface, CNTs have to be stabilized in aqueous suspension in order to avoid aggregation that reduces the active surface.
Conventional desalination methods are energy-consuming and technically demanding, whereas adsorption-based techniques are simple and easy to use for point-of-use water purification devices, yet their capacity to remove salts is limited. Yan HY, developed plasma-modified ultralong CNTs that feature an ultrahigh specific adsorption capacity for salt (exceeding 400% by weight) that is two orders of magnitude higher when compared with conventional carbon-based water treatment systems. These ultralong CNTs can implement in multifunctional membranes that are able to remove not only salt but also organic and metal contaminants. Next-generation potable water purification devices equipped with these novel CNTs are expecting to have superior desalination, disinfection, and filtration properties.
Polymeric nanoadsorbents
Polymeric nano adsorbents such as dendrimers (repetitively branched molecules) are utilizable for removing organics and heavy metals. Organic compounds can be adsorbed by the interior hydrophobic shells, whereas heavy metals can be adsorbed by the tailored exterior branches accordingly.
Zeolites
Chunke Water Treatment R&D teams are working on Zeolites for very long time. We have got some good result, but still it need times to be commercial to be used in water supplies.
Zeolites in combination with silver atoms have been known since the early 1980s. Zeolite has a very porous structure in which nanoparticles such as silver ions can be embedded. There they are released from the zeolite matrix by exchange with other cations in solution. Egger compared various materials containing nano-silver, including zeolites. When used for sanitary purposes, the silver attacks microbes and inhibits their growt.
Nanometals and nanometal oxides
Nanoscale metal oxides are promising alternatives to activated carbon and effective adsorbents to remove heavy metals and radionuclides. As well as having a high specific surface area, they feature a short intraparticle diffusion distance and are compressible without a significant reduction of surface area.To get more info about nanometals mentioned in What’s new in water treatment article, you can contact with us.
Nanosilver and nano-titanium dioxide
Nanosilver has been used in the photo development process since the late 1800s, and has been registered with the Environmental Protection Agency for use in swimming pool algaecides since 1954 and drinking water filters since the 1970s. Although nanosilver exhibits a strong and broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity, it has hardly any harmful effects in humans. It is already applied to point-of-use water disinfection systems and antibiofouling surfaces. Nano-titanium dioxide (TiO2), featuring high chemical stability and low human toxicity at a cheap price, is utilizable in disinfection and decontamination processes.
Photocatalytic water purification technology
Latest water purification technologiesA demonstration machine of photocatalytic water purification technology developed by Panasonic. Credit: Panasonic Corporation. Water treatment using photocatalysis has gained prominence in recent years due to its efficiency in treating contaminated water. The technology utilises photocatalyst and ultraviolet (UV) rays to remove toxic substances from water.
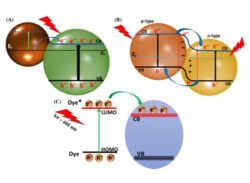
Panasonic developed a technology that binds the photocatalyst (titanium dioxide) to a commercial adsorbent and a catalyst called zeolite, ensuring effective separation and recovery of photocatalysts from the water for reuse. So, titanium dioxide can mineralize a range of organic compounds into safe end products. So, the catalyst uses UV radiation either from sunlight or artificial light to separate substances. In what’s new in water treatment article, photocatalytic water purification is one of the important newest technology.
Photocatalysis can break down a range of organic materials, estrogens, pesticides, dyes, crude oil, and microbes such as viruses and chlorine-resistant pathogens, as well as inorganic compounds such as nitrous oxides.
Photocatalytic water treatment systems are suitable for use in water and wastewater treatment facilities and can treat industrial wastewater polluted with high loads of organic substances or metals accordingly.
Aquaporin Inside technology
When people search, what’s in water treatment, they face with Aquaporin. Aquaporin Inside technology incorporates aquaporin proteins to replicate nature’s own water filtration process. Specialist water channels, aquaporin proteins exist in the membrane of all living cells. They can be found in every living organism, from plants and animals to human beings, and are essential to all life on Earth.
Placed within the cell membrane, aquaporin proteins transport water – and only water – in and out of the cell. Billions of years of evolution have made them extremely efficient and highly selective, like a superhighway for water. They are far better than any manmade water filter. One square meter of synthetic manmade membrane can filter around 50 liters of water per hour.
Automatic variable filter technology (AVF)
Automatic variable filter technology is a simple water filtration technology in which the downward flow of filter media cleans the upward flow of influent. It removes the need for freshwater or additional cleaning process for filter media cleaning. Two sets of media filters are integrated into a two-stage configuration that can function in parallel or serial mode. Automatic variable filter technology offers several advantages: it consumes less power, lower operating and maintenance costs, and no moving parts. It delivers quality equivalent to micro-filtration technology and gives the result at a much lower cost than the low-pressure membranes.
We explain some newest water treatment technologies in our what’s new in water treatment article.
If you have question or you want to learn more, please contact with us by filling in our contact form in below.
Chunke is leading water treatment company from China and we follow new water treatment technologies very close and apply in our designs.





